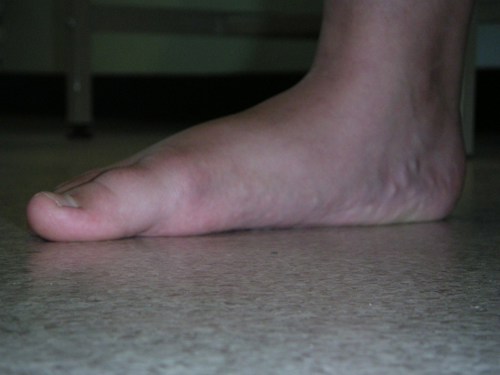
Flat Feet
A few important points
- Flat Feet are common in healthy babies and toddlers and usually resolve by 6 years of age as the longitudinal arch develops.
- Flat Feet persist in at least 10% of children, commonly are found with other features of hypermobility and are often familial (check parents feet !!).
- Management involves explanation, reassurance, and advice regarding appropriate supportive footwear (i.e., supportive heel cup and mid-foot support with fastened laces).
- Physiotherapists, orthotists and podiatrists may provide exercises and insoles if problems persist.
Photo: Flat feet in a healthy 4 year old - the medial arches form when standing on tip-toe - (mobile flat feet). Note that the changes are symmetrical.
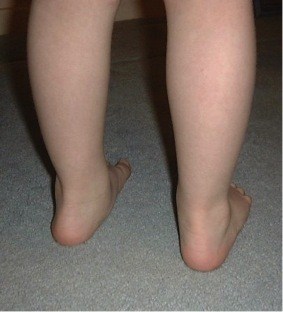
When should flat feet warrant concern?
- If there is an absent arch when the child stands on tip-toes ('non-mobile flat feet').
- There are asymmetrical changes (i.e., one foot fixed and flat).
- There is evidence of pressure on the foot such as blistering / callosities.
- There is swelling or restriction of joints.
- There is Limping observed or the child has persistent pain.
- In teenagers with a fixed/painful flat foot, think of Tarsal Coalition which is a condition where bones in the foot are fused together.
- Inflammatory Arthritis can also cause a painful stiff flat foot. Radiographs can be unremarkable. Referral is required for further investigation.
The indications for referral are:
- Joint stiffness or swelling.
- Absence of arch on tip-toe.
- Signs of pressure (e.g., blistering).
- Persistent pain.
- Limp or symptoms interfering with function (sport/play).
- Systemic features.
Referral is advised to rheumatology or orthopaedics. Conditions to consider are:
- Inflammatory Arthritis – joints are stiff, warm or swollen (often the midfoot).
- Tarsal Coalition – joints fixed and painful on walking and weight bearing.
Photo: Stiff Flat Foot due to Inflammatory Arthritis (Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis).