Normal Skeleton
The skeleton is important for posture, movement and protection of vital structures.
The hip and shoulder are 'ball and socket' joints that optimise movement. The knee and elbow are hinge joints. The ankle and wrist joints allow movement in several different directions. The spine comprises different sections - cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacrum.
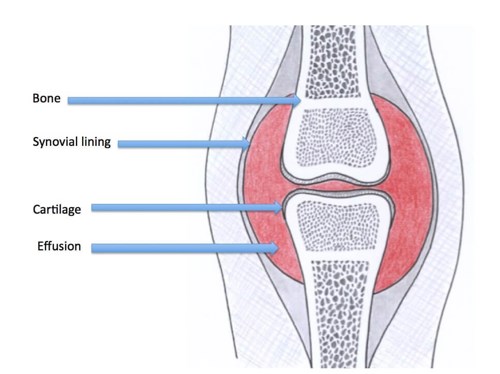
The normal joint - A joint is where two or more bones meet. Synovial joints are joints that have a synovial membrane. All synovial joints have the same components:
| The components of normal joints and their function Synovial fluid lubricates the jointCartilage reduces friction and is a shock absorberSynovial lining produces synovial fluid (An effusion occurs with inflammation)Tendon joins muscle to bone enabling movement and joint stabilityLigament joins bone to bone, stabilising the joint |