Describing Bone Joint and Muscle
Descriptions of bones, joints and muscle are important to aid accurate documentation of disease involvement - at the time of diagnosis and also as part of monitoring.
Descriptions are useful when communicating with colleagues (such as telephone advice).
We provide examples relevant to musculoskeletal disease
- Surface anatomy of key joints
- Joint movements of key joints (how these are described and normal ranges of movement)
Some useful terms
- Arthritis - refers to inflammation of joint(s) and is typified by pain, swelling, warmth, tenderness and limited movement.
- Arthralgia - refers to painful joints without overt swelling.
- Myalgia - refers to muscle pain but usually without tenderness or weakness.
- Myositis - refers to muscle pain and tenderness, often with weakness.
- Enthesitis - refers to inflammation at sites of insertion of tendon, muscle or fascia. Common sites of enthesitis are shown below;
- Effusion - refers to swelling of a synovial joint
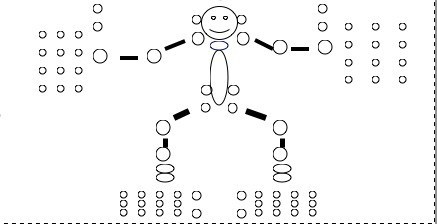
- Joint count - the number of joints that are swollen or have restricted range of movement or both. A homunculus can be used in clinical practice or as part of clinical trials to mark swollen joints or restricted joints. An example is given below;