Juvenile Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Juvenile Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (JSLE) is rare but is more common in non-caucasians, with a predominance of girls affected in the adolescent group and a more equal sex distribution in young children.
The arthritis of JSLE is usually polyarticular, often the pain is the major symptom but there is little objective swelling.
Extra - articular features are variable, and a diagnosis of JSLE is made with a combination of clinical and laboratory features (which are summarised below).
Common presenting symptoms of JSLE:
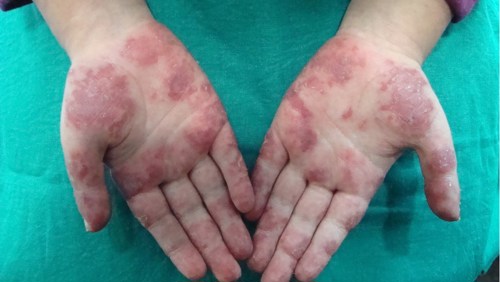
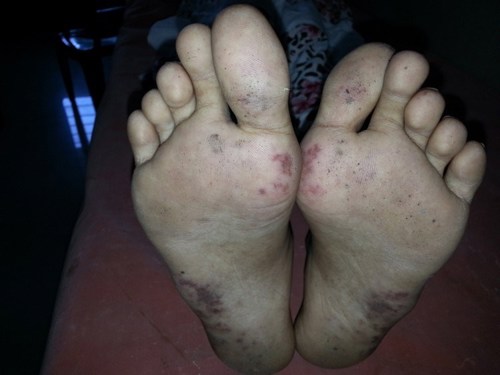
- Skin - Malar rash (photosensitivity), Alopecia, vasculitis rashes, Raynaud ’s phenomenon.
- Arthritis - polyarticular (small joints mainly).
- Systemic features - Fatigue / Fever / Weight loss / Oral ulcers.
- Pleuritis/pericarditis.
- Central nervous system (e.g., headaches, seizures, psychosis).
- Lymphadenopathy.
- Hepatosplenomegaly.
- Hypertension, peripheral oedema, facial puffiness (periorbital oedema).
Laboratory findings:
- Anaemia (may be haemolytic with positive red cell autoantibodies).
- Leukopaenia, lymphopaenia, thrombocytopaenia.
- Elevated liver enzymes.
- Elevated kidney function tests (blood urea nitrogen, creatinine).
- Abnormal urinary sediment.
- Decreased complement components C3 and C4.
- Positive antinuclear antibody (ANA).
- High titre positive anti-double stranded (ds) DNA antibody.
- Other positive autoantibodies (anti-Ro (SSA); anti-La (SSB); anti-Sm; anti-RNP).
- Positive anti-phospholipid antibodies (anti-cardiolipin, lupus anticoagulant).
Drug - induced JSLE can develop from the use of anti-convulsants, oral contraceptives or minocycline.
The medical management of JSLE is complex and requires specialist supervision, with nearly all patients requiring corticosteroid and immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, patients often require anti-hypertensives, anti-coagulation (related to anti-phospholipid syndrome), and medications to control dyslipidaemias and avoid osteoporosis (e.g., calcium & vitamin D).
The photographs below show skin vasculitis in JSLE.